Over the past century, advances in nutrition and medicine have contributed to a rise in life expectancy. However, as societies age, more people develop degenerative and lifestyle-related health problems. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), these non-communicable diseases (NCDs)account for 75% of all fatalities globally. These illnesses affect tens of millions of people worldwide and can significantly lower their standard of living. The financial effect is also enormous; a report by the Harvard School of Public Health and the World Economic Forum estimates that five leading NCDs (cardiovascular disease, chronic respiratory disease, cancer, diabetes and mental health) diseases could cost the world economy $47 trillion by 2030.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern healthcare, digital health has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing how we access, manage, and deliver medical services. At the core of this digital transformation lies the concept of data integrity. As the foundation of digital health, data integrity ensures that health data is accurate, consistent, and reliable, fostering trust and precision in healthcare practices. In this article, we explore the critical role of data integrity in shaping the future of digital health and how it adds value to the entire healthcare ecosystem.
Non-communicable disease is a term that applies to a chronic condition that is not contagious. These diseases have genetic, lifestyle, societal or environmental causes rather than viral or bacterial, usually resulting in long-term health issues. Health conditions that are considered non-communicable include cancer, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Non-communicable diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for 41 million deaths each year. This accounts for 71% of all deaths globally. The number of cases of diabetes, for example, has risen from 108 million in 1980 to 422 million in 2014 (WHO). The prevalence of diabetes has been rising more rapidly in middle- and low-income countries.
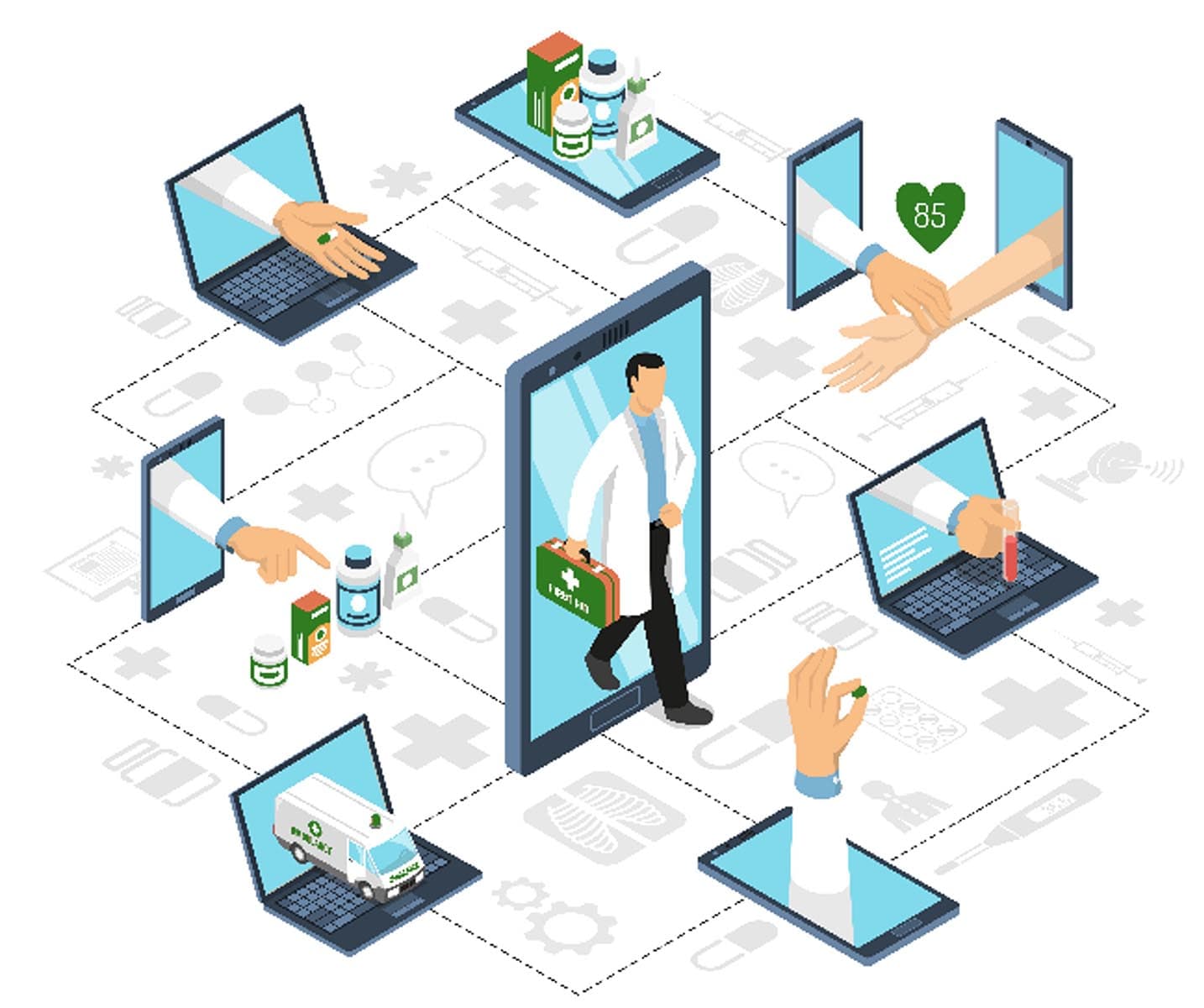
Linking digital transformation with the development of the health status of people worldwide leads to the promising topic of digital health. According to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), digital health includes categories such as mobile health (mHealth), health information technology (IT), wearable devices, telehealth and telemedicine, and personalised medicine.
Digital health types
-
Mobile Health
Mobile health (mHealth) is a rapidly expanding field providing support, delivery, and intervention in healthcare via mobile technologies such as smartphones, tablets, and different wearables. Currently, over 100,000 mobile health apps are available for users to download. Those apps can be used to track, record, and connect data and guide many aspects of health care.
-
Health IT
Health IT, which stands for health information technology, uses computer hardware, software, or infrastructure to record, store, protect, and retrieve clinical, administrative, or financial information. It often includes electronic health and medical records. Health IT is the area of Information technology involving the design, development, creation, use and maintenance of information systems used in the healthcare industry. The primary purpose is to improve medical care and public health, lowering costs, increasing efficiency, reducing errors, and improving patient and healthcare provider satisfaction.
-
Wearables
Wearables or wearable technology is any electronic device designed to be worn on a user’s body, with the most known examples being Fitbits and smartwatches. They are used for all sorts of reasons, but in healthcare, wearables are made to gather information about users’ health and exercise. They can even transmit a patient’s real-time data to a physician or healthcare expert. The most common data gathered is users’ step number, heart rate, calories, temperature and sleeping cycle. Simultaneously, some more advanced devices collect information about users’ blood sugar levels, alcohol levels, and UV exposure via special epidermal sensors.
-
Telehealth
Telehealth is exchanging medical information to improve a patient’s health status. It is also referred to as telemedicine, telecare, or virtual health. It offers a remote form of health care that is usually perceived as more convenient and accessible. Telehealth includes virtual sessions or video calls between the physician and the patient, but also telephone calls, remote patient monitoring, exchange of photographs and even interpretation of test results.
-
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is a form of medicine that incorporates knowledge about a patient’s genes or proteins to treat, diagnose, or prevent illness. Personalized medicine, as opposed to traditional medicine which uses a one-size-fits-all approach, considers the specifics of each person’s biology.
Importance of DI (Data Integrity) in Digital Health
Trends toward searches for specific medical symptoms are increasingly used to help identify and react to disease outbreaks by monitoring keyword activity on social media and search engines. This knowledge is helpful to any organization working in the health field, but it can also benefit any employer trying to maintain a healthy workforce. If the data are interpreted correctly, a large employer may be able to make a variety of preparations, such as ordering more tissues in case of a cold outbreak or hiring more freelancers to cover absent employees. The effect can be enormous when the algorithms correctly predict these trends, but significant obstacles must be overcome.
The FDA defines data integrity as “the completeness, consistency, and accuracy of data. Complete, consistent, and accurate data should be attributable, legible, contemporaneously recorded, original or a true copy, and accurate.”
Data Integrity not only concerns computer systems, equipment, and processes of pharmaceutic production but is also a hot topic of medical health. Maintaining the accuracy of a patient’s personal information, health summary, clinical notes, test findings, and family information are just a few examples of how this can be applied to healthcare. A system for keeping an electronic health record (EHR) must make meaningful, accurate, and complete data easily accessible so that clinical pathways can be developed, put into practice, and optimized to help with better clinical administration. As a result, data integrity is what drives EHR systems and is crucial to providing services at all levels.
Apart from data integrity, data security should also be considered when it comes to patient data. Data security guarantees that authorized administrators and healthcare professionals can connect to a patient’s data without difficulty while preventing unauthorized access to those records. Data security and integrity are intertwined.
Conclusion
According to a study done by Accenture, almost 60% of patients would prefer to use telehealth technology for accessing their healthcare information than walking to a doctor’s office. That means all the patient’s information will soon be saved and stored somewhere in the cloud. That is where data integrity and data security come in. Patient information uploaded to servers should be accurate and not modifiable by anyone for physicians to make the most precise diagnosis possible, as well as secure to maintain the maximum privacy of the patient.
Today’s patients seek quick, individualized, and easy access to care. It is time for healthcare companies to visit their patients in their homes – in a setting, location, and time where patients feel most comfortable – rather than forcing them to commute to a doctor’s office or care facility and endure the agony of waiting in a waiting room for hours. Sadly, many healthcare organizations lack the digital expertise and resources they require. It is time for these businesses to seek assistance and work with a dependable partner for digital transformation to realize the full potential of digital technologies and reinvent the meaning of personalized care.
As digital health continues to reshape the healthcare landscape, the significance of data integrity cannot be overstated. By safeguarding the accuracy and reliability of health data, data integrity paves the way for enhanced patient care, informed decision-making, and seamless interoperability among healthcare systems. From personalized medicine to innovative research, data integrity empowers healthcare professionals to harness the full potential of digital health and drive advancements in patient outcomes. As we move forward into the era of data-driven healthcare, the unwavering commitment to data integrity will remain the cornerstone of a transformative and patient-centric healthcare journey.
References
https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Harvard_HE_GlobalEconomicBurdenNonCommunicableDiseases_2011.pdf
Non-Communicable Disease: What is it and How Does it Work? (webmd.com)
https://www.fda.gov/medicaldevices/digitalhealth
https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-is-telehealth-5115712
https://www.verywellhealth.com/mobile-health-4014014
https://themoderndatacompany.com/blog/data-management/key-to-digital-transformation-in-healthcare/
https://www.ey.com/en_gl/digital/10-ways-digital-could-transform-healthcare
https://www.medicaldirector.com/news/data-security/why-data-integrity-is-critical-for-healthcare/
Photos from www.freepik.com
https://www.freepik.com/free-vector/illustration-social-media-concept_2807760.htm”>Image by rawpixel.com</a> on Freepik
https://www.freepik.com/free-vector/illustration-social-media-concept_2807760.htm?log-in=facebook
https://www.freepik.com/free-vector/online-medicine-network-isometric-infographic-template_6346051.htm”>Image by macrovector</a> on Freepik
KVALITO is a strategic partner, global quality and compliance service, and network for regulated industries. To find out more, please visit us at www.kvalito.ch. If you would like to benefit from KVALITO’s expert services, please send us an email: contact@kvalito.ch. Are you looking for an exciting and challenging position as a consultant, or maybe you are an ambitious student/graduate looking for an internship? Please send your complete application to recruiting@kvalito.ch.