What is ETL?
ETL, or Extract, Transform, Load, is a fundamental data integration and management process. Within the pharmaceutical and healthcare sphere, ETL plays a pivotal role in amalgamating data from diverse sources like EMRs, lab reports, billing info, and public health records. This process standardizes raw data into a uniform format, applying predefined business rules to cleanse, standardize, and normalize it for storage and analysis.
In the healthcare and pharma industry, the challenge lies in the diverse nature of data, including Electronic Health Records (EHRs), claims databases, medical devices, and clinical systems. This complexity often hampers analysis and sharing across organizations and research networks. ETL’s significance extends beyond Business Intelligence (BI) and reporting, impacting various data subjects and contributing to improved decision-making and industry insights.
The Applications of ETL in the Healthcare and Pharmaceutical Industry
- Clinical Research Networks: Participating in multi-site clinical research networks requires restructuring and transforming EHR (Electronic Health Record) data into a familiar format and standard terminologies. ETL processes can automate part of this transformation, facilitating data contribution to research networks [[1]].
- Data Pipelines and Analytics: ETL builds secure data pipelines, extracting, processing, and loading data from multiple sources. These pipelines leverage big data to enhance patient care, streamline operational operations, and improve decision-making [[2]].
- Real-time Insights: Optimizing ETL for real-time analytics is crucial for pharmaceutical professionals to gain timely insights from data, meeting the industry’s demand for swift data access [[3]].
- Data Integration and Management: ETL enables the integration of heterogeneous data sets from various sources, such as EHRs, medical devices, and clinical systems. By restructuring and transforming the data into a standard format, ETL facilitates effective data management, risk mitigation, patient safety, and informed decision-making [[4]].
- Quality Assurance: ETL testing ensures the integrity and reliability of healthcare data. By validating data, checking its completeness, and verifying compliance, ETL testing plays a vital role in maintaining data quality for decision-making related to patient health and other applications [[5]].
In summary, ETL processes are essential for data integration, standardization, and transformation in the healthcare and pharma industry, enabling seamless collaboration, data-driven insights, and improved patient care.
Why is ETL Important in the Pharmaceutical Industry?
A thorough understanding of the complex nature of healthcare data and its organization in the destination database is essential to answer health-related inquiries. The ETL process plays a crucial role in the healthcare industry as it facilitates the retrieval of data from the source system, which is typically an Electronic Health Record (EHR) and transforms it into a format that complies with the target database’s structure. This transformed data can be stored for future use or presented in a format ready for presentation. EHR data provides crucial information about patient’s health status and is a valuable information source for practitioners and researchers in the healthcare sector. EHR data helps improve patient outcomes and enables informed decision-making related to healthcare.
In the healthcare industry, ETL can range from essential data integration across various departments in a clinical setting to advanced integration of data from multiple Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems into Common Data Models (CDMs). Research networks primarily use these CDMs to share knowledge and facilitate research.
Integrating data from various sources in clinical science is a challenging task involving multiple ETL process iterations. These iterations can encounter challenges, such as inaccurate mappings, lengthy query times, and data quality issues. Conflicts between the source data and the destination system, where the source database may have different data representations, terminologies, data element terms, and data granularity levels, are common causes of incorrect mappings.
ETL Pipeline in Pharma: Managing Complexity for Efficiency
The ETL pipeline in the pharmaceutical sector often involves a series of critical procedures:
- Data Extraction and Preparation: The first step in the ETL process entails obtaining data from a particular source (diverse sources—medical claims, clinical studies, electronic health records (EHRs), and more), consolidating it, and preparing it for data integration. It is a process that amalgamates information from cloud applications, structured/unstructured files, on-premises databases, CRM systems, and cloud data warehouses. Compiling this diverse data demands sorting based on origin, date, and size to fit into the transformation process. The complexity escalates based on data volume, types, and sources.
- Data Transformation: The extracted data is transformed and standardized to guarantee accuracy and consistency. This step involves cleaning, filtering, eliminating duplicates, and rectifying discrepancies.
- Data Integration: Transformed data from diverse sources is combined into one singular database or data warehouse. This integration simplifies data analysis and utilization for business intelligence.
- Data loading: The final phase involves loading the analyzed data into a data repository for access by various stakeholders.
The concept of pipelining, where new data is extracted while old data transforms, is instrumental in the ETL process. Furthermore, modifications to the already-extracted data during loading into the data warehouse enhance flexibility and adaptability.
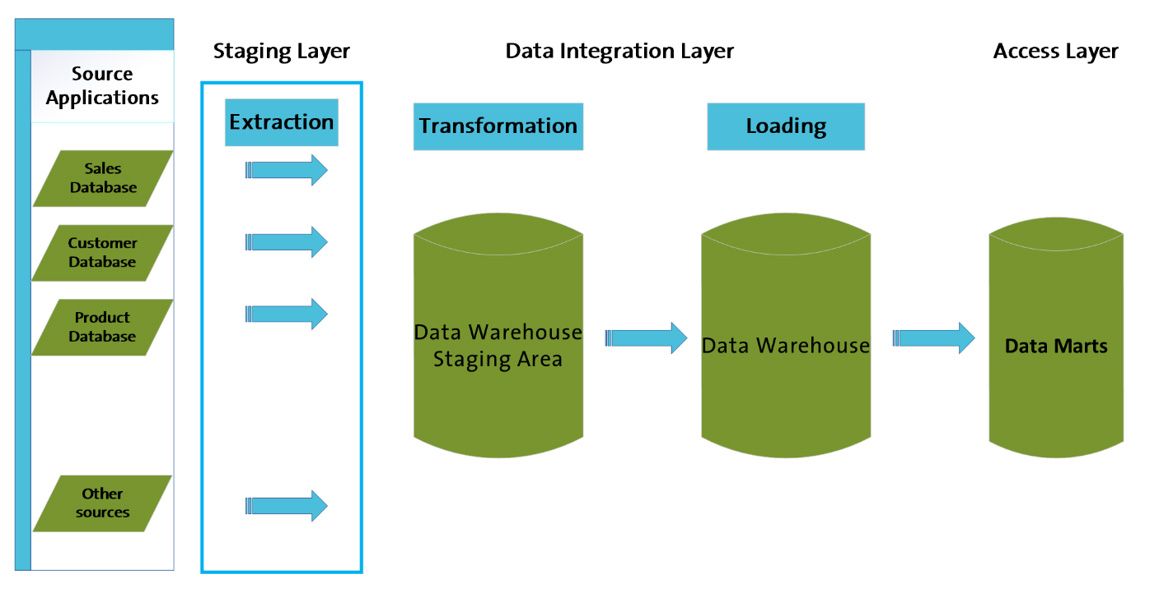
ETL in the Data Warehouse Architecture
Data extracted from various source systems is initially stored in the staging layer, a staging database. The integration layer transforms this data before it is directed to a database. This structured data includes facts tables, aggregate fact tables, and hierarchical groups (dimensions) gathered within a Data Warehouse (DW) system.
End users retrieve the data using the access layer for analytical reporting and information extraction.
ETL Challenges in Pharma
Several challenges hinder efficient ETL implementation within the healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors:
- Data Security and Privacy: Safeguarding sensitive patient data, clinical trial information, and intellectual property against unauthorized access and breaches remains a top priority. ETL processes must align with strict regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
- Data Complexity: The diverse nature of pharmaceutical data—from clinical trials to electronic health records and regulatory databases—poses extraction, transformation, and loading challenges due to variations in formats, structures, and semantics.
- Data Governance: Ensuring data quality, security, and regulatory compliance throughout the ETL process necessitates robust governance policies governing data management, storage, and utilization.
- Data Integration: The scattered nature of healthcare data across multiple systems makes creating a unified view challenging. Integrating legacy systems with modern ETL technologies demands substantial resources and expertise.
- Scalability: Given the enormous volumes of generated pharmaceutical data, scalable ETL processes become essential. Building robust infrastructure and monitoring systems is vital for efficient data management.
- Data Analysis: Extracting insights for informed decision-making requires specialized skills and tools. Pharmaceutical companies must invest in resources and training to leverage ETL-derived insights effectively.
In essence, these challenges underscore the technical expertise, resources, and effective governance necessary for successful ETL implementation within the pharmaceutical landscape. Data complexity, data quality issues, integration of legacy systems, data security and privacy, data governance, scalability, and data analysis must be addressed optimally to position healthcare organizations to leverage the potential of their data for enhanced patient care and increased operational efficiency.
Important considerations:
- Cost: The successful application of ETL can be a question of cost, especially for smaller businesses. Healthcare organizations must aim for affordable and scalable solutions as their needs change within an ever-evolving data landscape.
- Real-time Analytics: To make timely decisions, healthcare providers must have access to accurate and current information. However, integrating data for real-time analytics requires a solid and effective ETL process.
Novartis and the University of Oxford collaborated to develop an informatics framework to manage large volumes of multi-modal clinical trial data securely for advanced research purposes. A robust information security architecture was implemented to enable confidential data sharing between the pharmaceutical and academic partners. The privacy of over 50,000 patients’ clinical data was carefully protected through anonymization techniques while still preserving analytically valuable patterns. Specifically, specialized software was utilized to remove facial features and metadata from more than 230,000 MRI images during anonymization.
Throughout their designed ETL pipeline, comprehensive measures were taken to ensure data provenance, quality controls, and validation, guaranteeing accuracy and reproducibility in downstream statistical analysis. The heterogeneous data from various trials and modalities were transformed into a standardized relational structure to facilitate integrated analysis by a multi-disciplinary team. Additionally, the scalable nature of the framework allowed for the regular capture of new data from Novartis into a research-ready database at Oxford. This capability enables researchers to obtain novel insights into diseases through advanced analytics. To have a complete view of patient data, streamline operations, cut costs, raise the quality of care, and adhere to regulations, healthcare organizations must effectively address and master these ETL challenges.
Modern ETL Advancements Impacting Pharma Operations
There have been several trends of reformation and improvement in ETL in recent years. Here are two examples of them:
- Real-time Data Access for Pharma Analytics: In the dynamic domain of pharmaceutical analytics, instant access to real-time data stands as a game-changer. Conventional ETL methods often lead to data lag, rendering insights outdated. Simplifying access to live data holds immense potential for enhancing pharmaceutical functions across research, marketing, and patient-centric initiatives.
– Relevance: Big data strategies promise significant revenue growth in the healthcare sector. Minimizing insight lag is pivotal for mid-sized pharma entities seeking competitiveness without hefty investments. Adopting “streaming ETL” processes that enable real-time data processing offers scalability and performance, ensuring a competitive edge over traditional methods.
- Automated Data Quality Assurance: In healthcare, especially in pharma, data integrity is paramount due to its implications for public health and regulatory adherence. Implementing robust testing and scalable quality assurance solutions has become imperative.
– Approach: Employing high-volume data sampling amplifies verification capabilities. Conducting SQL-based comparisons between source systems and the data warehouse ensures the accuracy of case data. Using ETL code validation tools post-transformation, along with continuous integrity checks, solidifies data quality. Automation has resulted in a tenfold increase in testing coverage and a threefold decrease in testing time, enhancing overall efficiency.
These progressive trends—real-time data access and automated quality assurance—signify a shift toward improved operational efficiency, informed decision-making, and enhanced patient outcomes within the pharmaceutical landscape. Integrating these advancements into existing practices promises profound impacts on strategic initiatives and data-driven approaches for pharmaceutical stakeholders.
Conclusion: The Journey Towards Transformation in Pharma through ETL
While ETL is central to data retrieval and transformation in the pharmaceutical sector, ongoing challenges require innovative solutions in data security, integration, scalability, cost governance, and real-time analytics. Embracing modern trends like ETL automation and real-time testing is crucial for bolstering operational efficiency, reducing costs, and uplifting the standard of patient care.
Staying ahead in a competitive landscape necessitates a keen eye on evolving ETL trends. In a healthcare landscape increasingly reliant on data-driven insights, ETL remains the linchpin connecting raw data to actionable intelligence.
At KVALITO, our specialized ETL services cater to the pharmaceutical industry’s intricate needs. From end-to-end project management to regulatory-compliant system validation, our expertise spans IT quality management, ensuring data security, privacy, and risk mitigation.
We prioritize independent verification and validation, providing comprehensive audits for efficiency, effectiveness, and regulatory compliance. Our detailed reports optimize data management, ensuring your ETL processes perform optimally.
Our comprehensive ETL service empowers pharmaceutical data with precision. Collaborating closely with you, we ensure project success, delivering insights that enhance patient care, operational efficiency, and regulatory adherence. Contact us today to explore how our specialized ETL service unleashes the full potential of your data.
References:
- Ong, T. C., Kahn, M. G., Kwan, B. M., Yamashita, T., Brandt, E., Hosokawa, P., Uhrich, C., & Schilling, L. M. (2017). Dynamic-ETL: a hybrid approach for health data extraction, transformation and loading. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 17(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-017-0532-3
- ETL in Healthcare and Building Secure Healthcare Data Pipelines. (2023, May 30). https://hevodata.com/learn/etl-in-healthcare/
- (n.d.). Leveraging the Power of Real-time ETL for Better Pharmaceutical Insights. Www.rxdatascience.com. Retrieved December 5, 2023, from https://www.rxdatascience.com/blog/leveraging-power-real-time-etl-better-pharmaceutical-insights
- How Data Integration is Revamping Healthcare and Pharma. (2020, April 27). Data Integration Blog. https://dataintegrationinfo.com/data-integration-in-healthcare-pharma
- Gupta, M. (2022, April 13). The “secret sauce” for ETL testing in healthcare. HealthAsyst. https://www.healthasyst.com/healthcare-it-services/the-secret-sauce-for-etl-testing-in-healthcare/
- Reasons for Moving from Batch to Real-Time Analytics. (n.d.). Aiven. Retrieved December 5, 2023, from https://aiven.io/blog/why-you-should-think-about-moving-analytics-from-batch-to-real-time
- Automated ETL testing tool used in Pharmaceutical Firm. (n.d.). Global Analytic. Retrieved December 5, 2023, from https://lduservices.com/automated-etl-testing-tool-used-in-pharmaceutical-firm/
- Helping a Pharmaceutical Company Drive Business Insights Using ZS Accelerators on Amazon Redshift | AWS Partner Network (APN) Blog. (2021, February 15). Aws.amazon.com. https://aws.amazon.com/tw/blogs/apn/helping-a-pharmaceutical-company-drive-business-insights-using-zs-accelerators-on-amazon-redshift/
- ETL Process in Data Warehouse – GeeksforGeeks. (2019, January 25). GeeksforGeeks. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/etl-process-in-data-warehouse/
- Fatima, N. (2020, February 4). ETL Process: Transformation Steps & Significance In Business. https://www.astera.com/type/blog/etl-process-and-steps/
- ETL Testing – Quick Guide. (n.d.). Www.tutorialspoint.com. Retrieved December 5, 2023, from https://www.tutorialspoint.com/etl_testing/etl_testing_quick_guide.htm#
- Folorunsho, D. (2022, December 8). ETL in the Context of Clinical Data Science. https://towardsdatascience.com/etl-in-the-context-of-clinical-data-science-9236e399c88a
- Mallon, A.-M., Häring, D. A., Dahlke, F., Aarden, P., Afyouni, S., Delbarre, D., El Emam, K., Ganjgahi, H., Gardiner, S., Kwok, C. H., West, D. M., Straiton, E., Haemmerle, S., Huffman, A., Hofmann, T., Kelly, L. J., Krusche, P., Laramee, M.-C., Lheritier, K., & Ligozio, G. (2021). Advancing data science in drug development through an innovative computational framework for data sharing and statistical analysis. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-021-01409-4
KVALITO is a strategic partner, global quality and compliance service, and network for regulated industries. To find out more, please visit us at www.kvalito.ch. If you want to benefit from KVALITO’s expert services, please email us at contact@kvalito.ch. Are you looking for an exciting and challenging position as a consultant, or are you an ambitious student or graduate looking for an internship? We look forward to receiving your complete application at recruiting@kvalito.ch