Imagine receiving medical treatment from the comfort of your home, using technology to simulate a doctor’s visit or surgical procedure. This is now our reality that is rapidly evolving, thanks to the advances in Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technology!
AR and VR have the potential to revolutionize the healthcare industry by providing immersive and realistic experiences to deliver new types of treatments and diagnostics. This was especially relevant during the pandemic when virtual care gained unprecedented value. The healthcare sector is now witnessing a surge in investments and regulatory approvals for these technologies, changing the face of healthcare.
In this article, we will explore the latest advances in AR/VR in medicine and how they drive the adoption of these technologies in the healthcare industry.
What are AR and VR, and how are they transforming the medical device industry?
AR is a technology that overlays computer-generated images or information onto the user’s real-world environment. The AR virtual environment is designed to coexist with the natural environment. Conversely, VR is a fully immersive technology that transports the user to a simulated virtual environment that can be explored and interacted with through a VR headset or other equipment.
The first VR medical device was created in the 1990s and was primarily used for surgical training. However, with the advancement of technology, the application of AR and VR in medicine has expanded significantly. Their impressive capabilities have increased interest in medical extended reality (MXR) devices.
MXR devices have demonstrated specific benefits for patients and healthcare professionals, such as:
- Improved patient outcomes: AR and VR can provide physicians with better visualization, allowing for more precise diagnoses and improving patient outcomes.
- Enhanced medical education and training: Medical students can use AR and VR devices to simulate medical procedures and reduce preoperative anxiety.
- Reduced medical errors: AR and VR can help reduce medical errors by allowing physicians to observe the patient’s anatomy closely and plan the best course of action.
- Increased patient engagement: AR and VR can help patients understand their condition and treatment options, improving patient engagement and better treatment adherence.
- Accessible healthcare: AR and VR devices can bring healthcare to underserved areas, providing patients with access to specialized care they may not otherwise have.
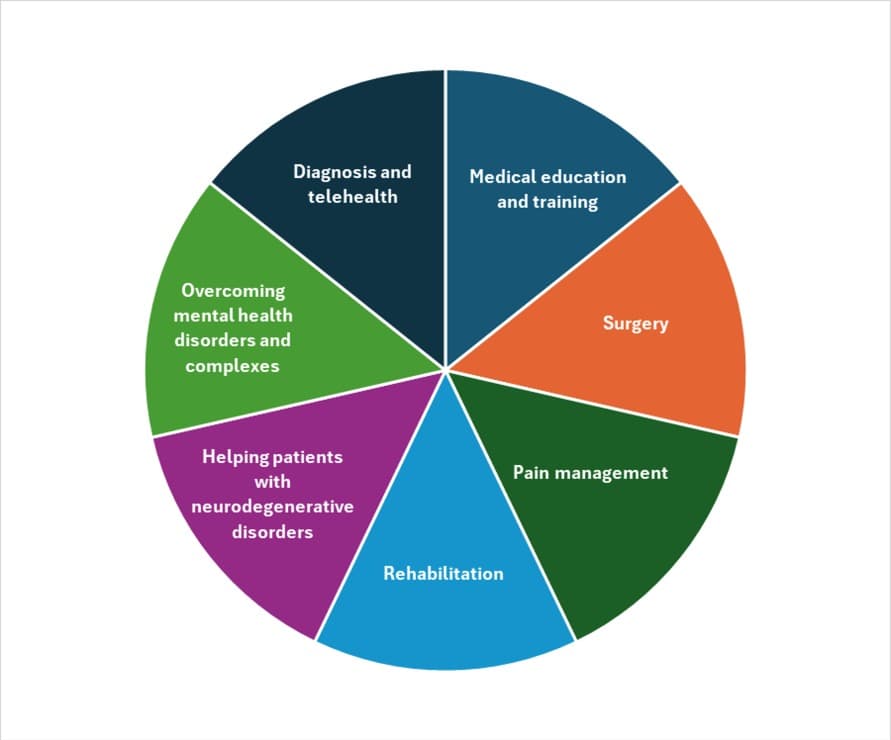
Applications of VR & AR in medical devices
Augmented reality and virtual reality have found a multitude of applications in treating patients across various domains.
Medical education and training
VR and AR effectively facilitate theoretical learning for medical students and healthcare professionals. Such learning environments may be applied to anatomy instruction, medical procedure simulation, medical device training, and interprofessional education. It helps them acquire hands-on skills in risk-free conditions by simulating difficult, dangerous, or expensive scenarios and enables planning for future operations. This way, the use of training dummies and cadavers is minimized.
Surgery
AR surgical navigation systems help guide surgeons during surgery. Using cutting-edge tools like 3D imaging, computer-assisted planning, and real-time monitoring, surgical navigation systems have improved results by enabling surgeons to precisely find and visualize a patient’s anatomy during surgical procedures. AR surgical navigation systems have been particularly beneficial in neurosurgery, orthopaedic and spine surgery, and laparoscopic surgery due to improved accuracy, reduced risk of complications, and shortened operating times.
Pain management
VR helps lower the level of pain or extreme discomfort by diverting a patient’s attention to a soothing virtual environment and minimizing the use of potentially harmful painkillers. It is also effective as an alternative method of pain relief and can also be used during childbirth as a substitute for epidural anaesthesia and other drugs.
Rehabilitation
Various illnesses can lead to severe damage to the brain, limbs, and nerves that can deteriorate motor skills. Patients can regain these skills using virtual reality. VR transforms therapy sessions into a gamified experience, encouraging them to achieve virtual goals. Patients can relearn how to carry out their daily tasks in the virtual environment, aiding their recovery.
AR-based rehabilitation can simulate real-world activities and adjust the difficulty level of tasks based on the patient’s progress, making it personalized and adaptive. AR-based rehabilitation can stimulate reflexes and problem-solving skills. Additionally, patients can practice balance and coordination drills in a secure and monitored setting, reducing the risk of injuries.
Helping patients with neurodegenerative disorders
With AR technology, people with neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease can improve their quality of life through cognitive stimulation and social interaction. AR technology-created virtual social settings help enhance attention and analytical skills.
Scientists have already proven the positive effects of VR for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease and relieving its symptoms. For example, Cambridge University researchers designed and implemented a navigation test that uses virtual reality to detect patients with early Alzheimer’s and is more reliable than a conventional cognitive assessment.
Overcoming mental health disorders and complexes
Virtual reality can be effectively applied in psychotherapy to treat various phobias and mental health conditions. Technology allows doctors to create a controllable environment and put patients in conditions preset individually for each case to train them to overcome their fears and gain confidence.
Post-traumatic stress disorder is another condition that can be effectively treated using virtual reality devices. The immersive experience provided by VR can also be used as a relaxation therapy to deal with various anxieties and stress-related disorders.
Diagnosis and telehealth
AR medical devices can monitor patient data in real time and provide remote access to medical information. They help healthcare providers gather vital information about a patient’s condition, such as reports and statistics, and visualize symptoms through full-body scans. AR technology is also used for thermal imaging, which was especially useful during the COVID-19 pandemic to assess a patient’s temperature without physical contact.
This technology is also used for telehealth and reduces costs associated with physical visits. In telehealth visits, AR devices can enhance the patient experience and enable doctors to consult with patients remotely.
AR and VR have tremendous potential to transform the medical device industry, there are still challenges to overcome, such as cost, integration with existing systems, and ensuring patient data privacy and security. However, as technology advances, we can expect to see more innovative applications of AR and VR in healthcare, leading to improved patient outcomes and better medical device solutions.
Top VR medical devices
- MindMotion Pro: A VR system developed by MindMaze that specializes in rehabilitation to help patients recover from stroke and other neurological conditions. It is designed to improve patients’ motor, cognitive, and emotional functions by providing interactive and engaging activities in a virtual environment.
- Osso VR: A VR platform for immersive surgical training and education for medical professionals. Osso VR creates virtual simulations of real-life surgeries, allowing healthcare professionals to practice their skills and receive real-time feedback.
- Psious: A VR-based platform for various mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders, phobias, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It offers a more engaging and effective alternative to traditional talk therapy and tools for therapists to create personalized VR environments for their patients.
- Luminopia: A VR platform that provides therapeutic treatments for children who suffer from amblyopia (also known as “lazy eye”), a condition that affects the visual development of the brain. The virtual world is designed to stimulate both eyes differently, which can improve visual acuity and depth perception.
- RelieVRx: A VR therapy system developed by AppliedVR designed to provide pain management and relaxation for patients in healthcare settings. RelieVRx offers a range of VR experiences that target specific types of pain and anxiety, including chronic pain, acute pain, and pre-surgical anxiety.
- EYE-SYNC: A VR platform to help diagnose and treat concussions and other brain injuries. The platform provides objective, data-driven assessment of brain health. It includes eye-tracking technology that can detect subtle changes in eye movement that may indicate a brain injury.
Top AR medical devices
- Intellirod Spine’s iLink System: This system employs augmented reality to give surgeons real-time feedback during spine fusion operations. It has sensors that can track alterations in the load and strain placed on the patient’s spinal hardware. The surgeon may then modify the positioning of the apparatus as necessary, thanks to the AR system’s overlay of this data onto their view of the patient.
- Philips Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation: During minimally invasive surgeries, this device employs AR to provide surgeons with a 3D map of the patient’s inside anatomy. It may be utilized for various operations, including liver and prostate surgeries.
- Microsoft HoloLens: It is a head-mounted augmented reality tool that adds digital pictures to the surgeon’s field of view as they examine the patient. Placing implants, soft tissue treatments, and surgical planning may all be done using it.
- AccuVein AV400: This device employs augmented reality (AR) to highlight the skin’s veins, making it simpler for the surgeon to find veins during procedures like blood draws and IV insertions.
- CAE VimedixAR: With augmented reality, this device gives medical students and residents a detailed simulation of ultrasound-guided surgeries. It enables the student to practice conducting operations like central line installation and ultrasound-guided nerve blocks by superimposing virtual pictures onto a real mannequin.
- Proximie platform: It uses augmented reality (AR) for remote collaboration and support during surgical procedures. The software connects on-site surgeons with distant medical specialists using augmented reality, enabling them to collaborate in real-time while performing surgery. The remote medical expert may join the live broadcast via the Proximie platform and give the surgeon advice and support.
Challenges for AR and VR medical devices
Several challenges need to be addressed for the widespread adoption of AR and VR medical devices:
- Cybersickness: This type of motion sickness is caused by the disconnect between what the user sees and what they feel. It can cause nausea, headaches, and dizziness.
- Head and neck strain: The weight of the headset and prolonged use can cause pain and strain in the neck and head.
- Cybersecurity and privacy risks: Medical data is highly sensitive. Data protection and privacy regulations need to be strengthened when developing MXR devices.
- Lack of assessment tools: More tools are needed to assess and clinically validate the usability, technical capabilities, and safety of AR/VR medical devices. This also makes the regulatory process lengthy and complicated.
- Cost: AR and VR devices require high computing power and advanced graphics capabilities, which can be costly and complex to manufacture. This limits their availability and accessibility to specific regions and populations.
- Unknown side effects and/or risks (particularly in vulnerable populations): AR/VR technology is still in its early stages, and there may be unknown side effects, long-term effects, or risks, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children, older people, and those with pre-existing medical conditions.
Overcoming challenges and embracing opportunities
Some exciting areas where AR medical devices show great potential are assisted-surgery, advanced diagnosis, medical imaging, and chronic disease management. On the other hand, the use of VR medical devices in telemedicine is already expanding, with the ophthalmology and mental health sectors witnessing significant changes. Furthermore, such devices are being explored for clinical trials. These technologies have the potential to provide a more convenient and comfortable experience for patients while also improving the accuracy and efficiency of data collection.
However, as with any new technology, some challenges must be overcome to ensure their effectiveness, safety, and accessibility. Fortunately, researchers and developers are already working to improve the technology, prioritize user-centred design, collaborate across disciplines, gain regulatory approval, and provide education and training. As these challenges are overcome, we can look forward to a future where AR and VR medical devices play an increasingly important role in improving patient outcomes and advancing medical science.
References
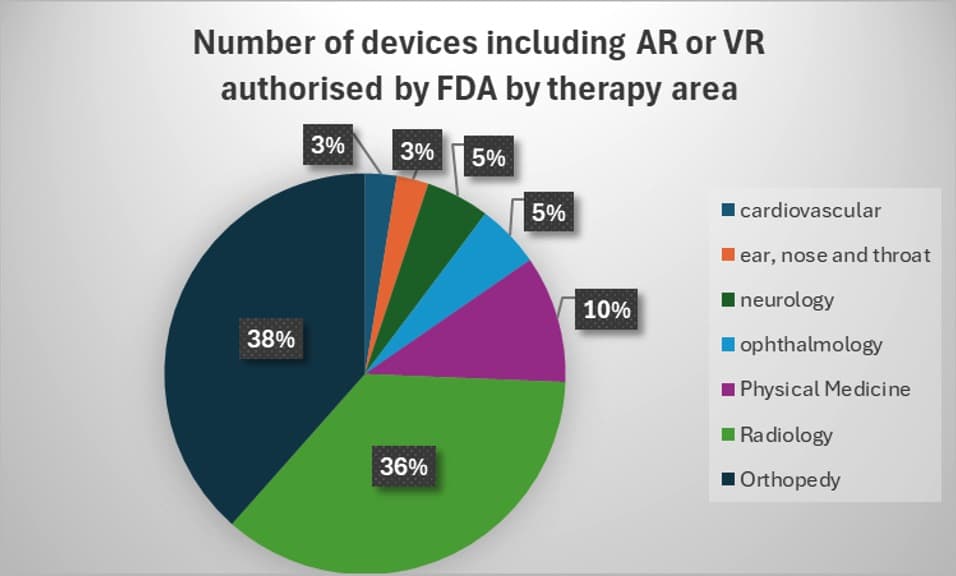
- https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/digital-health-center-excellence/augmented-reality-and-virtual-reality-medical-devices
- Virtual and augmented reality applications in medicine: Analysis of the scientific literature. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 23(2). Yeung, A.W. et al. 2021.
- Real-time computer-generated integral imaging and 3D image calibration for augmented reality surgical navigation. Wang, J. et al. March 2015, Vol. 40.
- https://www.fiercebiotech.com/medtech/reality-check-ar-and-vr-are-poised-to-send-medtech-into-next-dimension-2022
- https://jumpgrowth.com/ar-vr-in-healthcare-benefits-use-cases-cost/
- Surgical Navigation Systems Based On AR/VR Technologies. Vladimir Ivanov, Anton Krivtsov, Sergey Strelkov. 2021.
- https://light-it.net/blog/virtual-reality-in-medicine/
- https://www.scnsoft.com/virtual-reality/healthcare
KVALITO is a strategic partner, global quality and compliance service, and network for regulated industries. To find out more, please visit us at www.kvalito.ch. If you want to benefit from KVALITO’s expert services, please email us at contact@kvalito.ch. Are you looking for an exciting and challenging position as a consultant, or maybe you are an ambitious student/graduate looking for an internship? Please send your complete application to recruiting@kvalito.ch.